

To Cemetry
One of the most unusual features of the Qumran site is the cemetery. More than a thousand people were buried along the eastern ridges of Qumran. The graves that have been excavated have raised many questions. Were there women at Qumran?
Learn more
Kitchen
Food preparation and preservation are not easy in the harsh conditions of the Judean Desert. The Qumranites faced the additional challenge of their own special diet and purity restrictions.
Learn more
Main Gate
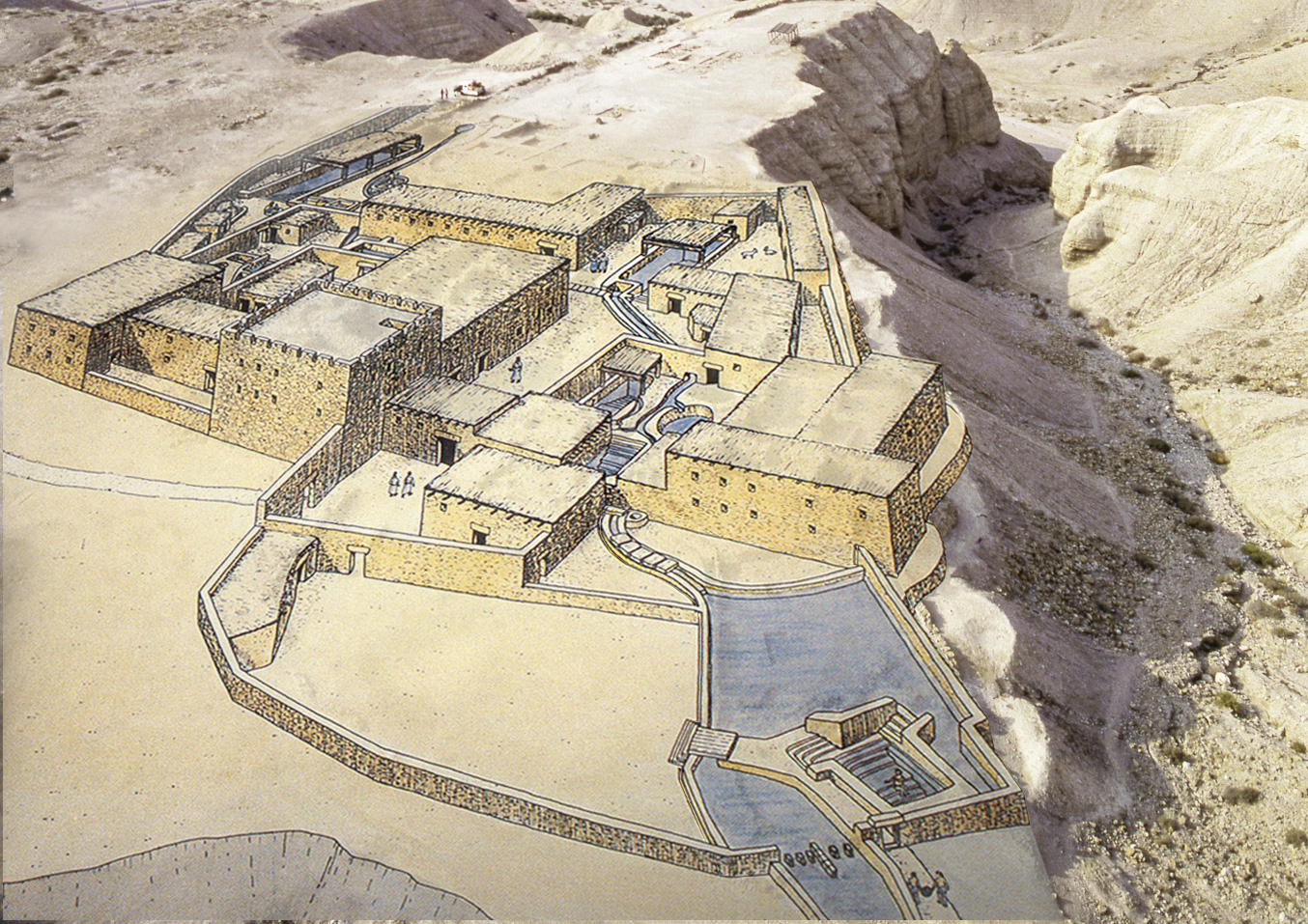
The Qumran complex is situated on the northwest shore of the Dead Sea, about 13 miles (20 km) east of Jerusalem. Anyone who came to the complex entered through this gate, which was overlooked by a strong defense tower.
Learn more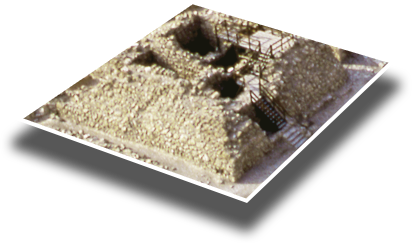
Tower
From here you can see the surroundings of Qumran. The Dead Sea, the cliffs of the Judean Desert and the road from Jerusalem are all in view. Through the Main Gate just below, all visitors entered the site.
Learn more
Scriptorium
The inkwells found in this room hint that scribes worked here to produce and copy scrolls. Could this be the source of some of the hundreds of ancient scrolls found in the nearby caves? .
Learn more
Assembly Hall
The largest room of the Qumran settlement has been identified as an assembly hall. Community members may have gathered here several times daily for prayers, meals, and community meetings
Learn more
Pantry
Over a thousand serving utensils and vessels were found here. Hundreds of simple bowls and plates had fallen off the shelves in an earthquake and shattered on the ground. Afterwards they covered and never moved
Learn more
To Caves
In the winter of 1947, a Bedouin shepherd found a few scrolls in a cave near Qumran. Since then, hundreds of scrolls have been found in eleven caves near the site. What are the connections between the caves and the site?
Learn more
Water System
Water means life. The Qumran region receives very little rain. Floodwaters were caught by a manmade dam and brought by aqueduct to the site, where the water was stored in large cisterns for drinking and ritual washing. .
Learn more